Meet with the best CRPS physical therapists in Novi, Michigan
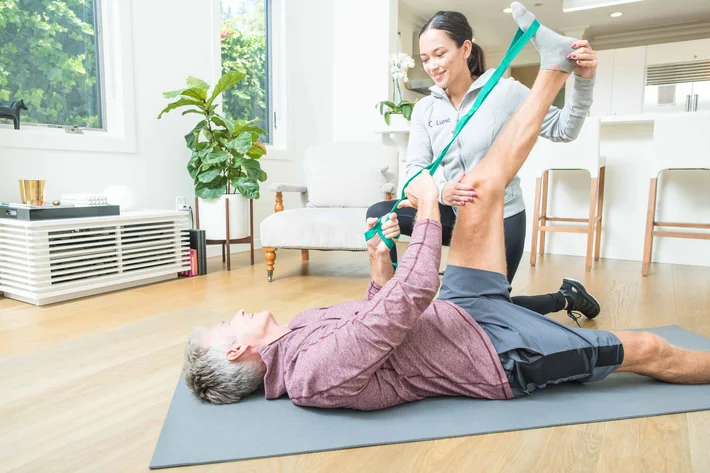
Novi, Michigan, Luna employs a talented group of physical therapists who specialize in treating patients suffering from CRPS. Our PTs will work with each patient to design a dynamic physical therapy routine that will retrain the affected limb — and ideally stop the condition’s progression in its tracks.
Best of all, with Luna, patients can receive physical therapy right in the comfort of their own homes. Our physical therapists come to you — it’s physical therapy, delivered.

What is CRPS?
Complex regional pain syndrome, or CRPS, refers to a type of chronic pain that tends to affect one limb at a time. It typically develops after a traumatic event such as an injury, a stroke, a heart attack, or surgery. CRPS is distinguished by pain that’s out of proportion with the severity of the triggering event.
CRPS is relatively uncommon, and the cause isn’t completely understood. However, the condition can vastly improve with treatment, especially when the condition is detected and treated early. In these cases, complete remission is a strong possibility.
Patients with CRPS tend to experience a continuous burning or throbbing sensation in the affected body part, typically a leg, arm, hand, or foot. They may also experience swelling or stiffness, as well as heightened sensitivity to touch or cold sensations. Patients who experience these symptoms should contact a doctor immediately, as early treatment is vital for recovery.
Source: Mayo Clinic

What causes CRPS?
Though the exact cause of CRPS isn’t known, it’s been known to occur after a traumatic event such as an injury, stroke, heart attack, or surgery. For this reason, it’s believed to occur due to an injury to the peripheral and/or central nervous systems.
There are two types of CRPS. Type 1, which is also known as reflex sympathetic dystrophy syndrome, occurs after an illness or injury that did not directly damage the affected limb. About 9 in 10 people with CRPS have Type 1. Type 2, the rarer form of CRPS, occurs following a distinct nerve injury in the affected limb.
The most common causes of CRPS include:
- Stroke
- Heart attack
- Injury
- Surgery